Influences of Ethanolic Extract of Peltophorum pterocarpum Leaves and Bark on Lipid Profile, Liver and Carbohydrate Metabolizing Enzymes on Toxin-induced Wistar Rats
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/fra.2023.1.6Keywords:
Peltophorum pterocarpum, Liver enzymes, Lipid profile, Carbohydrate metabolizing enzymes, Isoniazid, RifampicinAbstract
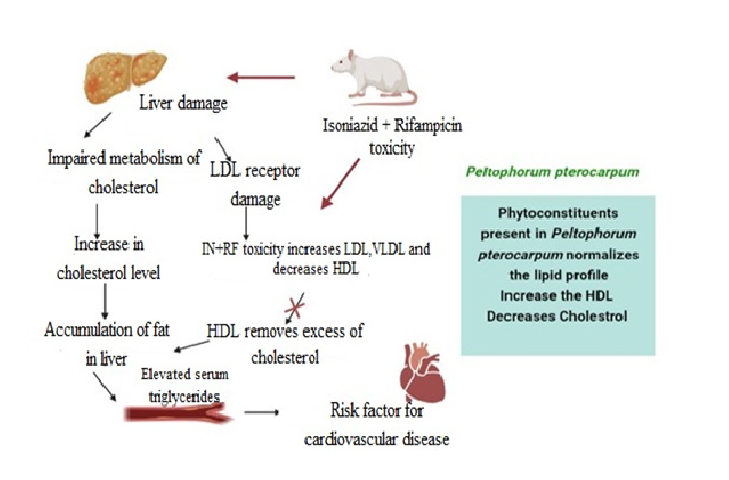
Background: The study was to identify the effects of ethanolic extract of Peltophorum pterocarpum leaves and bark on lipid profile, liver and carbohydrate enzymes on isoniazid and rifampicin induced Wistar rats. Materials and Methods: Ethanolic leaf and bark extract of P. pterocarpum freshly suspended in sterile water (300mg/kg BW), were administered to rats post-orally as a single dosage orally by intubation early morning for each day of the experimental period. Rats were separated into 10 groups with 6 rats in each group and maintained in isolated cages with proper ventilation. The samples were introduced to find the following parameters Total Cholesterol (TC), Triglycerides (TG), Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, Very-Low-Density Lipoprotein (VLDL) cholesterol, Phospholipids (PL), Free Fatty Acid (FFA), Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST), Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT), Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP), glucose, glucose-6-phosphatase, glucose-6- phosphate dehydrogenase and hexokinase, kidney markers such as urea, uric acid and creatinine. Results: The results highlighted that the leaves and bark extract of P. pterocarpum had a potential hepatoprotective effect against the toxin treated rats and may alter lipid profile, liver and carbohydrate metabolizing enzymes levels. Conclusion: This effect proves the hepatoprotective nature of both the leaves and barks of P. pterocarpum.
Downloads
Metrics