Evaluation of Antioxidant Activity of Psidium guajava Linn. in streptozotocin–Induced Diabetic Rats
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/fra.2016.1.9Keywords:
Catalase, Glutathione peroxidase, Lipid peroxides, Psidium guajava, Reduce glutathione, Superoxide dismutaseAbstract
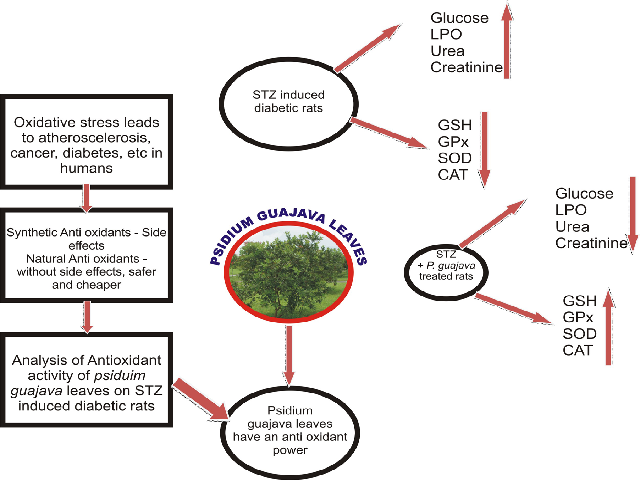
Background: The incidence of diabetes is increasing rapidly in world wide. It produces disturbances in the metabolism of carbohydrate, protein, and lipid. Evidences recommended that the natural medicines originating from plant source may represent a culturally relevant complementary treatment for diabetes. Objective: The aim of the present study is to investigate the antioxidant activities of the ethanolic leaf extract of Psidium guajava Linn. in streptozotocin (STZ) induced oxidative stress in rats. Methods: Oxidative stress is induced with a single dose of STZ 60 mg/kg b.w. and then the animals are treated with a dose of various concentrations of ethanolic leaf extract of P. guajava (100 mg/kg b.w, 200 mg/kg b.w, and 300 mg/ kg b.w) for 45 days. After the treatment, the glucose, lipid peroxides (LPO), reduce glutathione (GSH), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), urea and creatinine levels are determined. Glibenclamide is used as a standard drug (3 mg/kg b.w.). Results: The present study exposed that the administration of ethanolic leaf extract of P. guajava showed a significant decrease in glucose and LPO levels. The treatment also finds that the significant increase in GSH, GPx, SOD and CAT levels in the liver, when compared with diabetic control rats. Conclusion: The results proved that the ethanolic leaf extract of P. guajava treated group may effectively regulate the antioxidant status in STZ induced diabetic treated groups.
Downloads
Metrics