GC-MS/HPTLC Analysis, Antioxidant, Anti-inflammatory and Antimicrobial Efficacy of Garcinia cambogia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/fra.2023.1.3Keywords:
Garcinia cambogia, GCMS, HPTLC, Antibacterial, Antioxidant, Anti-inflammatory.Abstract
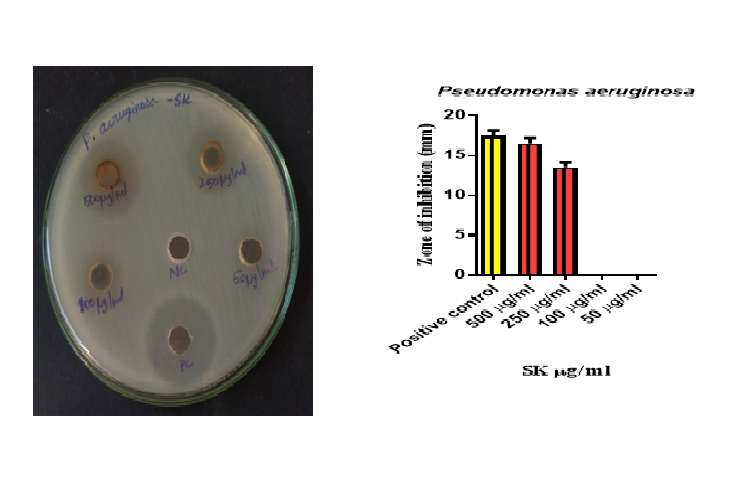
Background: Natural substances that were initially obtained from plants were once regarded as a beneficial source of possible medicinal agents and were recognized as crucial in the development of human diseases. The current study sought to determine whether hydroalcoholic extracts of Garcinia cambogia plant fruits included any bioactive substances. Materials and Methods: The plant fruits were collected, shade-dried, ground into a fine powder, and then extracted using Soxhlet extractors and organic solvents. After that, the extracts were examined for the presence of phytochemicals using GC-MS/HPTLC, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antibacterial techniques. According to the GC-MS studies, the hydroalcoholic extracts of G. cambogia contained 25 bioactive components. Results: The secondary metabolites identified in the plant, discovered by GCMS/HPTLC, are what give the plant extracts their powerful medicinal qualities. The results of the antimicrobial activity demonstrated outstanding antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties as well as effective dose-dependent inhibitory activity against all of the tested species. Conclusion: The current study provided early data on the bioactive components present in G. cambogia fruit extracts, which have outstanding antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory action, which could provide a significant platform for pharmaceutical companies to create different Garcinia species-based medications.
Downloads
Metrics