Anti-oxidant capacity, total phenolic contents and HPLC determination of rutin in Viola tricolor (L) flowers
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ax.2012.4.6Keywords:
Anti-oxidant activity, HPLC, Rutin, Viola tricolorAbstract
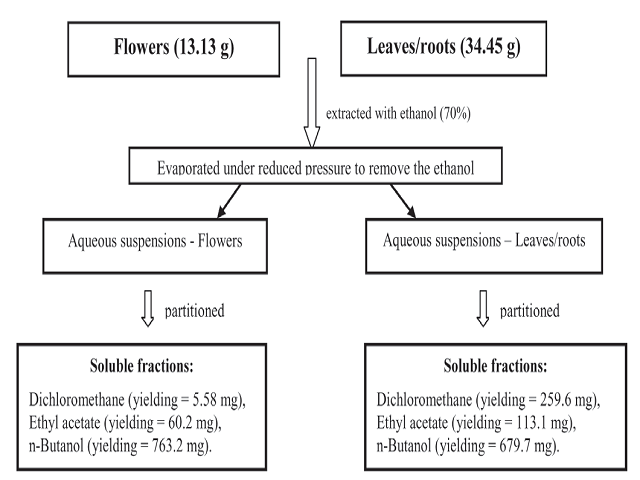
Background: Natural products with anti-oxidant properties have gained importance in recent years due to their ability to neutralize free radicals or their actions. Viola tricolor belong to Violaceae family and is known as heartsease. The aims of the study was to evaluate the phenolic contents and anti-oxidant capacity in the different flowers and leaves/ roots fractions of Viola tricolor, as well as was identified and quantify rutin in the flowers fractions. Materials and Methods: Total phenolic content was determined using the Folin-Ciocalteu assay, the anti-oxidant capacity by the 1, 1-diphenyl-2-picryl-hydrazyl (DPPH) scavenging method and thiobarbituric acid reactive species (TBARS) assay. The presence of rutin was investigated by High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC). Results: In the flowers fractions the phenolic content varied from 12.84 ± 0.072 to 0.23 ± 0.042 mg/g; and 7.49 ± 0.002 to 0.63 ± 0.002 mg/g for leaves/roots. IC50 DPPH values ranged from 13.40 to 14.18 mg/ml in flowers, and 32.84 to 284.87 μg/ml for the leaves/roots. The fractions showed inhibition against TBARS, following order: ethyl acetate fractions > butanolic fractions > dichloromethane fractions. HPLC results indicate a very high content of rutin (177.46 mg/g) in this species that could explain the good anti-oxidant activities and the high phenolic contents in these fractions. Conclusions: These findings suggest that V. tricolor contains anti-oxidant principles and rutin contribute, in party, for the action.
Downloads
Metrics