2,3,4-Trihydroxybenzoic Acid, an Antioxidant Plant Metabolite Inhibits Cancer Cell Growth in vitro: Potential Role in Cancer Prevention
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/fra.2024.2.8Abstract
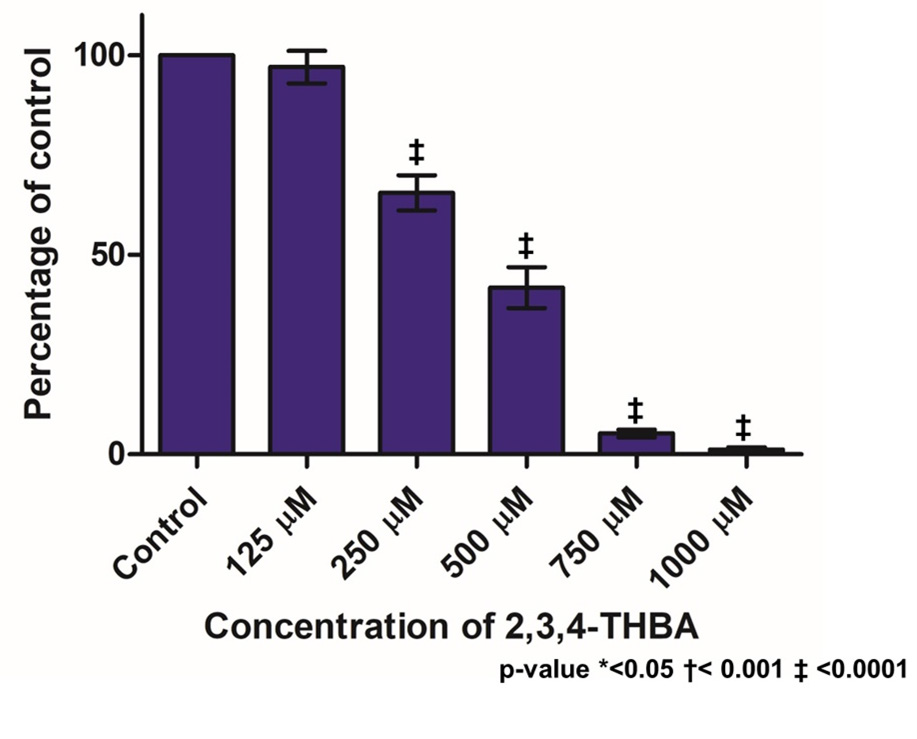
Background: Colorectal Cancer (CRC) is the third most common cause of cancer death in the US and more than 1 million people are diagnosed with this disease every year worldwide. In this regard, flavonoids and their degradation products, namely Hydroxybenzoic Acids (HBAs) continue to be evaluated for the prevention of CRC. Hydroxybenzoic acids are also present as secondary plant metabolites in many fruits and vegetables. In the present study, we determined the ability of 2,3,4-THBA, which is present in fruits and vegetables and known to have antioxidant properties, to inhibit cancer cell growth in HCT-116 colon and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Materials and Methods: Cell proliferation assays and clonogenic assays were carried out to determine the effect of 2,3,4-THBA on cancer cell growth. Cell morphology was determined using light microscopy. Western Blot experiments were performed to determine the expression levels of Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-type 2 (HER2), Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor (FGF-R), Cyclin-Dependent Kinase (CDK) inhibitors p21 and p27. In silico studies were performed to determine the potential binding of 2,3,4-THBA to CDK1, CDK2, CDK4 and CDK6. Results: We demonstrate that 2,3,4-THBA dose-dependently inhibited HCT-116 colon and MDA-MB-231 cancer cell proliferation. It also significantly decreased the colony formation in both cancer cell lines. Treatment of cells with 2,3,4-THBA did not alter the levels of HER-2 and FGF-R; however, it induced the levels of expression of CDK inhibitors p21 and p27 in a dose-dependent fashion. In silico studies suggested that 2,3,4-THBA has the potential to bind to CDK1, CDK2, CDK4 and CDK6 through interactions with specific amino acids. Conclusion: The growth inhibitory effect of 2,3,4-THBA on cancer cells may occur partly through induction of CDK inhibitors p21 and p27, and through direct binding to CDKs involved in cell cycle regulation. These data suggest that 2,3,4-THBA from plant sources has the potential to be used in cancer prevention.
Downloads
Metrics