Cardioprotective Potential of Qusqualis indica Leaves; An in silico Docking Study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/fra.2023.1.7Keywords:
Quisqualis indica, Cardio-protective, in silico.Abstract
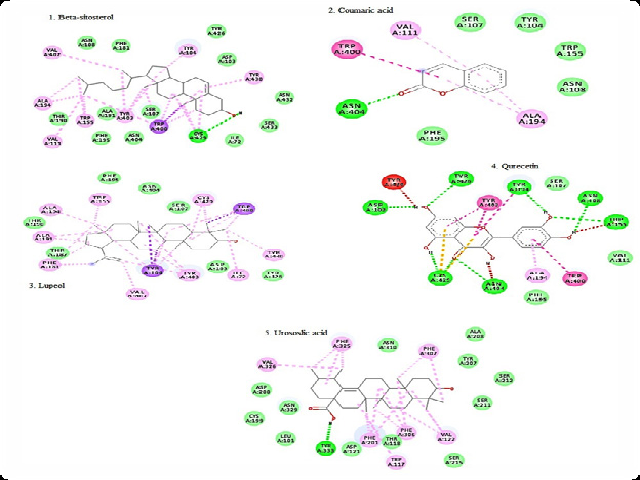
Background: Nowadays cardiac problems are the main cause of death. It includes coronary artery disease, angina pectoris (stable and unstable), congestive heart failure, etc. Objectives: The aim of this paper was to generate scientific data regarding In silico analysis of beta-sitosterol, coumaric acid, lupeol, qurecetin, and urosolic acid of Muscarinic (M2) receptor. Materials and Methods: The leaf powder was treated with different reagents and prepared with different extracts. The phytochemical screening was carried out by treated the extracts with different reagents for the presence of various metabolites. RCSB protein data bank had used for docking studies. Results: The phytochemical screening clearly revealed the presence of various metabolites like flavonoids, alkaloids, saponins, etc. In-silico analysis of beta-sitosterol, coumaric acid, lupeol, qurecetin, and urosolic acid had very good interactions with cholinergic receptor (M2). The obtained score is -7.96, -5.63, -6.7, -7.73, -5.82 for beta-sitosterol, coumaric acid, lupeol, quercetin, and urosolic acid, respectively, which lies in the standard scale. Conclusion: All these metabolites (compounds) are present in Quisqualis indica leaf extracts (aqueous and ethanolic) and found to be good cardio protective agents.
Downloads
Metrics