Antioxidant activity of Mokkathotapapada leaves of Piper betel L. Cv. Kapoori
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ax.2012.4.12Keywords:
Antioxidant, DPPH, FeCl3, Nitric oxide, Superoxide and Phenolic compoundsAbstract
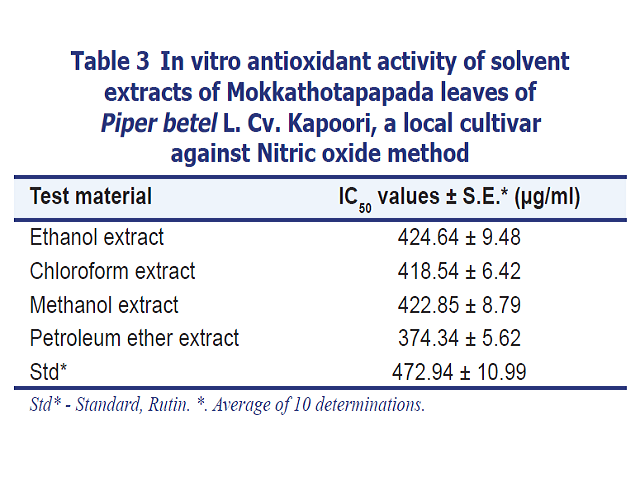
Introduction: Ingredients of Indian cuisine are well known for their antioxidant properties which can help prevent many diseases. The Betel (Piper betel L.) is the leaf of a vine belonging to the Piperaceae family; it is figured out both as a mild stimulant and for its medicinal properties. The betel plant originated from South and South East Asia. The leaves of Piper betel L. have been traditionally known for its various therapeutic uses. Piper betel L. Cv. Kapoori is a local cultivar obtained from Chintalapudi, Guntur district of Andhra Pradesh, India, but their antioxidant properties have not been investigated. Methods: Organic solvent extracts of Mokkathotapapada leaves of Piper betel L. Cv. Kapoori was determined by DPPH free radical scavenging activity, reducing power by FeCl3, nitric oxide free radical scavenging activity, super oxide scavenging activity.Also used specific standard for each test. Results: Solvent extracts of Mokkathotapapada leaves of Piper betel L. Cv. Kapoori were compared with the light of respective standard drugs and the extracts were found to be equipotent with the standards in all the tested methods. Conclusion: Presence of phenols and phenolics (Chavicol, Chavibetol, Chavibetol acetate and Eugenol) in the Mokkathotapapada leaves of Piper betel L. may be credulous to be responsible for its antioxidant activity.
Downloads
Metrics