Chemical composition and antioxidant activity of the ethanol extract and purified fractions of cadillo (Pavonia sepioides)
Keywords:
Antioxidant activity , Pavonia sepioides , Reactive oxygen species , Free radicals , Oxidative stressAbstract
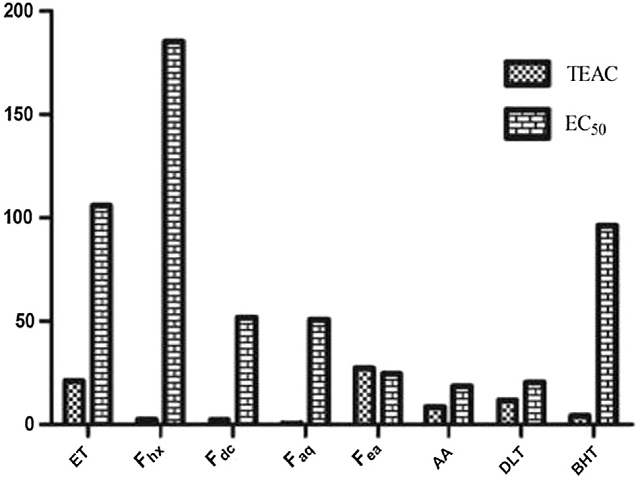
Background: Bioactive plant compounds can contribute to prevent diseases related to oxidative stress. Some of these compounds are water soluble and fat soluble vitamins, carotenoids and a huge variety of phenolic compounds associated with the antioxidant activity (AOA). Objective: The aim of this study was to study the antioxidant activity of Pavonia sepioides. Methods: The AOA was evaluated by spectrophotometric methods using the free radical DPPH* and the ABTS*þ radical cation assays. Total phenolic content (TPC) was determined by FolineCiocalteu method and total flavonoid content (TFC) was determined by direct reaction with aluminum trichloride. The phenolic content was evaluated by GC/MS technique. Results: The greatest antioxidant activity was found in ethyl acetate fraction (Fea), The total ethanol extract (TE) showed good AOA in comparison with hexane fraction (Fhx), dichloromethane fraction (Fdc) and aqueous fraction (Faq). The TPC and TFC analyses provided results consistent with the AOA with highest values for Fea and ET respectively. Different phenolic compounds of low molecular weight were identified by GC/MS (Salicylic acid, cinnamic acid, p-hydroxybenzoic acid, p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid, phydrocinnamic acid, vanillic acid, gentisic acid, p-cinnamic acid, o-Cinnamic acid, protocatechuic acid, syringic acid, m-cinnamic acid, ferulic acid, and caffeic acid). These compounds could be associated with the named activity. The Pearson and Spearman association tests indicated a positive linear correlation between the AOA and TPC and TFC results, showing correlation coefficients greater than 0.810 in the Pearson test and greater than 0.700 in the Spearman test (p < 0.05). Conclusion: The AAO of P. sepioides (ET and purified fractions) was confirmed. The study provides evidence that P. sepioides is potential source of natural antioxidants showing positive correlations between phenolic contents and the AAO.
Downloads
Metrics