Phytochemical Analysis of Cinnamomum zeylanicum Bark and Molecular Docking of Procyanidin B2 against the Transcription Factor Nf- κB
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/fra.2017.2.30Keywords:
Cinnamomum zeylanicum, Gold, Molecular docking, NF-κB, Procyanidin B2Abstract
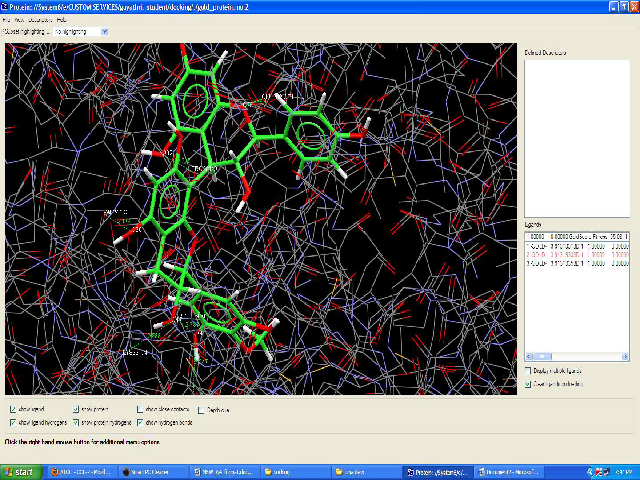
Introduction: Identification of novel natural antioxidant compounds is a highly demanding avenue of therapy for oxidative stress induced diseases. The bark of Cinnamomum zeylanicum commonly known as Ceylon cinnamon is commonly used in Ayurvedic medicine. Method: In this study, the methanolic extract of bark was subjected to GC-MS, UV absorption and TLC techniques to analyze the presence and to elucidate the structure of proanthocyanidins present in the bark. In the latter part of the study, chemdraw structure of the identified procyanidin B2 was subjected to in silico molecular drug docking analysis using GOLD to find out its inhibiting efficacy against NF-κB (1NFI). Results: The phytochemical analysis supported the presence of a proanthocyanidin compound, procyanidin B2. The constitutive or aberrant activation of the transcription factor, NF-κB pathway is often noticed in many cancers, autoimmune disorders, pulmonary, cardiovascular, neurodegenerative and skin diseases. The docking of procyanidin B2 with NF-κB revealed its inhibiting efficacy by binding to active site of NF-κB and thus could inhibited the nuclear translocation and DNA binding of p50/p65 heterodimer to κB DNA sequences. Conclusions: Thus, procyanidin B2 can act as the inhibitor for NF-κB. So, procyanidin B2 present in C. zeylanicum bark can be used as a potential lead compound for drug development against cancer and other oxidative stress disorders.
Downloads
Metrics