Antioxidant Potential of a Toxic Plant Calotropis procera R.Br.
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/fra.2017.2.21Keywords:
Calotropis procera, Free Radicals, ROS, DPPH, AntioxidantAbstract
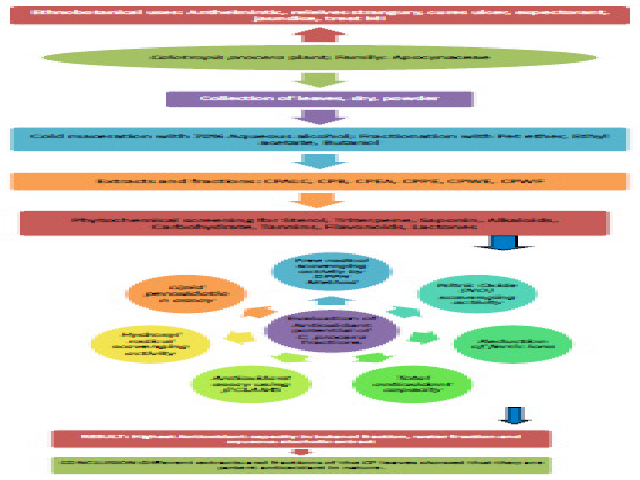
Background: Calotropis procera R.Br. (Family, Apocynaceae) is a toxic herb which was known to have great importance in the Ayurveda. The plant is anthelmintic; relieves strangury; cures ulcers; the ashes act as an expectorant. The plant was also known to be used in the treatment of jaundice from ancient times. Studies have shown that it has cardio-protective property in Myocardial Infarction. The present study was focused on evaluating the anti-oxidant activity of the leaves by in vitro models. Methods: The anti-oxidant activity in different extracts and fractions of the leaves viz. total alcoholic and water extracts; petroleum ether, ethyl acetate, butanol and water fractions were evaluated for antioxidant properties using various in vitro models like free radical scavenging activity, hydroxyl radical scavenging activity, nitric oxide scavenging activity, hydrogen peroxide scavenging activity, reduction of ferric ions and lipid peroxidation assay; and total antioxidant capacity was established. Results: Antioxidant potency was found to be highest in butanol fraction, water fraction and aqueous alcoholic extract. Conclusions: The antioxidant property of different extracts and fractions of the leaves were studied in vitro and results have shown that they are potent antioxidant in nature.
Downloads
Metrics