Involvement of attenuated antioxidant and Bcl2 signalling property in UV-R/ sunlight irradiated piperine treated ischemia/ reperfusion rat model
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/fra.2014.1.8Keywords:
Piperine, UV-R/sunlight, Cerebral Ischemia, NeuroprotectionAbstract
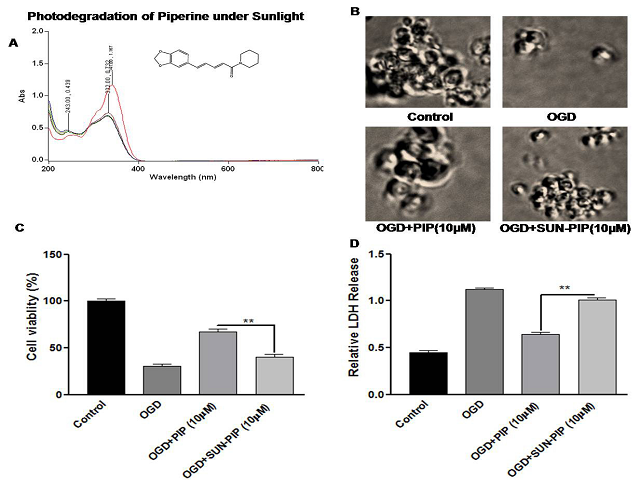
Introduction: Piperine (PIP) is well known multifunctional antioxidant and anti-inflammatory phytochemical that showed neuroprotection. Pre-treatment of UV-R irradiated piperine (UVR-PIP) 10 mg/kg body weight bw, intravenously showed attenuated neuroprotective effects compared to that of PIP (10μM) in PC12, cortical neuronal culture in-vitro and a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia in-vivo. Method: Neurological parameters were evaluated for UVR-PIP and PIP treated against transient focal cerebral ischemia of SD rats through quantification of infarct volume by TTC staining. In-vitro results deal with reduction of cell viability on UVR-PIP treatment in PC12 and cortical neuronal cell. The result of photodegradation of PIP under UV-R irradiation revealed the formation of photoproducts. Estimation of Mitochondrial ROS, antioxidant enzyme and non-enzyme activities in UVR-PIP and PIP treated brain tissue. Results: Results indicated OGD induced primary cortical neuron cultures and PC12 cells showed that SUN-PIP treatment decrease cell viability and increased LDH secretion compared to that of the PIP pre-treatment. In addition, Bcl-2 expression was decreases after the SUN-PIP treatment. Thus, our results demonstrated that SUN-PIP preconditioning failed to increase levels of Bcl-2 and normalized the endogeneous antioxidant, mediating the neuroprotective effects of PIP. UV-R irradiation attenuated the neuroprotective effects of PIP through modulation of the antioxidant and Bcl-2 mediated pathway. Conclusion: Thus, the ability of UV-R to serve as a modulator of this neuroprotective signaling pathway. Piperine loses some of its neuroprotective ability when irradiated by UV radiation and care has to be taken during storage to avoid exposing piperine to the sun.
Downloads
Metrics