Antioxidant Activity and Phenolics Analysis by HPLC-DAD of Solanum thomasiifolium Sendtner (Solanaceae)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/fra.2014.1.4Keywords:
Solanum thomasiifolium, Antioxidant activity, Total phenolic content, High performance liquid chromatography coupled with diode-array detector, FlavonoidAbstract
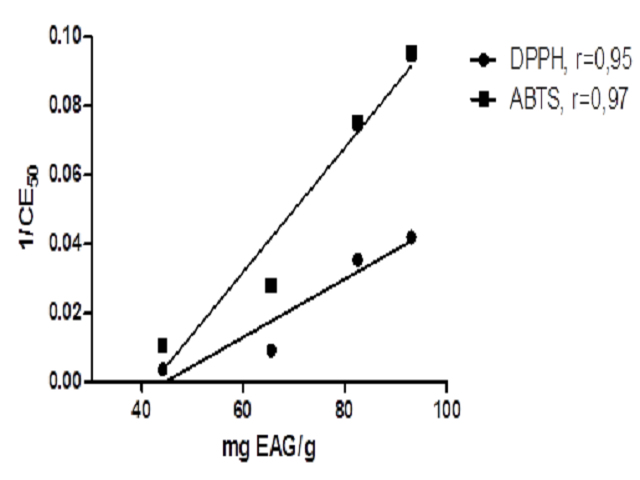
Introduction: The genus Solanum is the most representative of the Solanaceae families and is considered one of the largest and most diverse among the Angiosperms. Chemotaxonomic studies have recognised the genus Solanum as a source of phenolic compounds, which present a wide variety of biological actions, including antioxidant activity. Methods: The hexane, ethyl acetate, ethanol and aqueous extracts of aerial parts of the Solanum thomasiifolium Sendtner were studied for antioxidant activity by using different assay in vitro such as inhibition of DPPH, superoxide anions and lipid peroxidation. The total phenolic content in the extracts was analysed by the Folin-Ciocalteu method. In addition, the active extracts were fractionated by open column chromatography containing Sephadex LH-20 and the phenolic compounds presents in the fractions were analysed by High Liquid Chromatography coupled with diode array detector (HPLC-DAD). Results: The better results were ethanolic and aqueous extracts which exhibited good scavenging activity of DPPH (IC50 = 23.9±0.7 and 28.3±3.1 μg/mL), ABTS (IC50 = 10.5±0.4 and 13.3±0.5 μg/mL), β-carotene t = 60min (83.3±0.1% and 91.3±1.5 %), and phenolic content (93.0±6.9 and 82.5±1.4 mgEAG/g). The analysis of UV profiles obtained by HPLC-DAD showed the presence of flavones and flavonols in the active fractions. Conclusion: This work shows that polar extracts of S. thomasiifolium were good antioxidant activity.
Downloads
Metrics