Solvent Extract from Opuntia stricta Fruit peels: Chemical Composition and Biological Activities
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/fra.2015.2.2Keywords:
Antibacterial activities, Antioxidant activities, Non-polar compounds, Opuntia stricta fruit peels, Solvent extractionAbstract
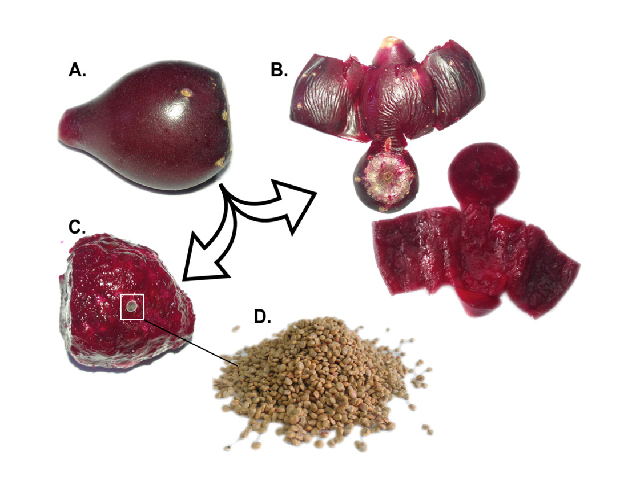
Background and aim: Opuntia stricta is belonging to the Cactaceae family. Its fruit is composed of around 69% peels, 21% pulp and 10% seeds. Extracting bioactive compounds from the peels; the major part usually discarded, helps to reduce the cost and environmental concerns associated with their disposal. Many studies have been interested in extracting dyes and phenolics from O. stricta peels, showing their antioxidant properties, but no work was devoted to extract and characterize the non-polar compounds meaning hydrodistillation. Method: O. stricta fruits were collected at ripening, the peels, pulps and seeds were manually separated. Peels were then blended, hydrodistilled, and the non-polar compounds were extracted and identified using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Afterwards, the antioxidant and antibacterial activities of the extracted molecules were investigated. Results: The extracted non-polar compounds from O. stricta fruit peels were mainly terpene alcohols. The major components were trans-linalool oxide, cis-linalyl oxide and linalool with 38.3%, 29.6% and 23.4%, respectively. The antioxidant activities showed high inhibition of the DPPH free radicals with 84% at 50 mg/ml, higher reducing power than that of ascorbic acid, and high total antioxidant activity with 309 ± 37 μg ascorbic acid equivalent at 25 mg/ml. The antibacterial activities showed high growth inhibition against Staphylococcus aureus and partial inhibition against Enterococcus faecalis. Conclusion: Non-polar compounds extracted meaning hydrodistillation from O. stricta fruit peels exhibit high antioxidant activities and inhibit the growth of S. aureus. They represent thus a promising way for the valorization of this by-product.
Downloads
Metrics