Evaluation of Lemon Peel Extract as Hepatoprotective Agent against Paracetamol-Induced Liver Toxicity: Insights from Biochemical Studies
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/fra.2024.1.2Keywords:
Hepatoprotective, Lemon Peel Extract, Paracetamol-Induced Liver Toxicity, Biochemical StudiesAbstract
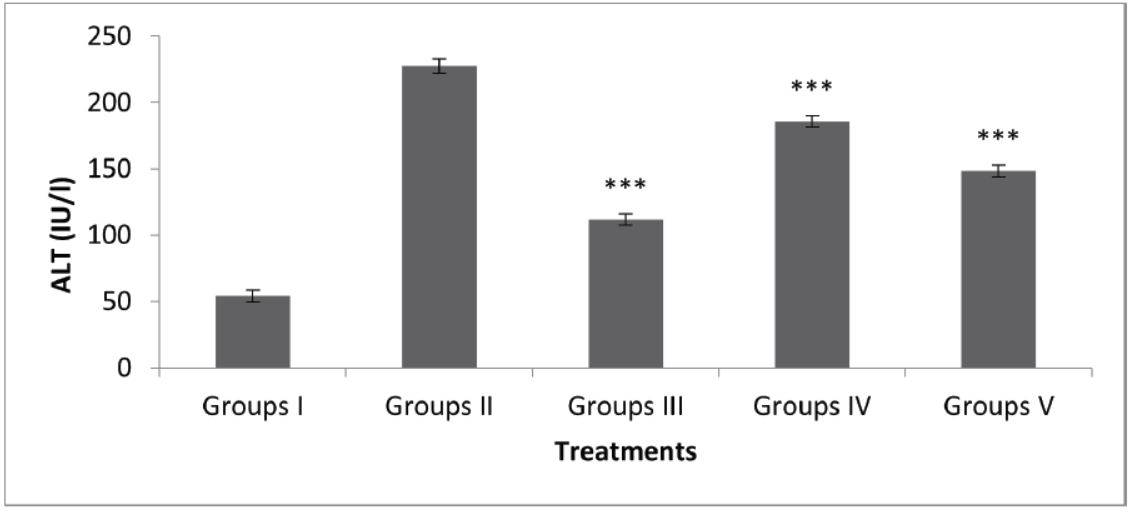
Background: The liver serves as a vital organ in metabolic processes and detoxification, making it susceptible to damage induced by xenobiotics such as drugs. Paracetamol overdose is a common cause of hepatotoxicity. Traditional medicine has long explored botanical sources for hepatoprotective agents, highlighting the potential of natural compounds in mitigating liver damage. Lemon peel, rich in flavonoids with antioxidant properties, presents a promising candidate for hepatoprotection. Materials and Methods: This study aimed to investigate the hepatoprotective effects of lemon peel extract on paracetamol-induced liver toxicity in rats. The extract was prepared through standardized extraction procedures and its dose was selected based on previous studies. Wistar rats were divided into five groups and subjected to various treatments, including paracetamol overdose with or without lemon peel extract supplementation. Biochemical parameters indicative of liver function, such as serum levels of AST, ALT, ALP and bilirubin, were measured following treatment protocols. Results: Administration of paracetamol alone induced significant elevation in serum levels of AST, ALT, ALP and bilirubin, reflecting hepatocellular damage. However, co-administration of lemon peel extract with paracetamol resulted in reduced levels of these biochemical markers compared to the paracetamol-only group. The decrease in enzyme levels suggests potential hepatoprotective effects of lemon peel extract. Conclusion: Lemon peel extract demonstrated hepatoprotective effects against paracetamol-induced liver toxicity in rats, as evidenced by the attenuation of biochemical markers indicative of liver damage. These findings highlight the therapeutic potential of lemon peel extract as a natural remedy for protecting liver health and mitigating the adverse effects of hepatotoxic agents.
Downloads
Metrics
References
Webb C, Twedt D. Oxidative Stress and Liver Disease. Vet Clin North Am-Small Anim Pract. 2008;38:125-35.
Banerjee P, Gaddam N, Chandler V, Chakraborty S. Oxidative stress-induced liver damage and remodeling of the liver vasculature. Am J Pathol. 2023;193(10):1400-14.
Garcia-Cortes M, Robles-Diaz M, Stephens C, Ortega-Alonso A, Lucena MI andrade RJ. Drug induced liver injury: an update. Arch Toxicol. 2020;94:3381-407.
Williams JA, Ding W-X. Role of autophagy in alcohol and drug-induced liver injury. Food Chem Toxicol. 2020;136:111075.
Rotundo L, Pyrsopoulos N. Liver injury induced by paracetamol and challenges associated with intentional and unintentional use. World J Hepatol. 2020;12:125.
Süntar I. Importance of ethnopharmacological studies in drug discovery: role of medicinal plants. Phytochem Rev. 2020;19:1199-209.
Wu C, Lee S-L, Taylor C, Li J, Chan Y-M, Agarwal R, et al. Scientific and regulatory approach to botanical drug development: A US FDA perspective. J Nat Prod. 2020;83:552-62.
Chaachouay N, Zidane L. Plant-Derived Natural Products: A Source for Drug Discovery and Development. Drugs Drug Candidates. 2024;3:184-207.
Singh B, Singh JP, Kaur A, Singh N. Phenolic composition, antioxidant potential and health benefits of citrus peel. Food Res Int. 2020;132:109114.
Bekkouch O, Zengin G, Harnafi M, Touiss I, Khoulati A, Saalaoui E, et al. Anti-inflammatory study and phytochemical characterization of Zingiber officinale roscoe and Citrus limon L. Juices and their formulation. ACS Omega. 2023;8:26715-24.
Rana R, Mehmood MH, Shaukat B, Shahid S, Malik A, Murtaza B. Evaluation of the Cardiovascular Effects of Coriandrum sativum and Citrus limon to Treat Arsenic-Induced Endothelial Damage and Hypertension in Rats. Life. 2022;12:1842.
Karn A, Zhao C, Yang F, Cui J, Gao Z, Wang M, et al. In vivo biotransformation of citrus functional components and their effects on health. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2021;61:756-76.
Harborne AJ. Phytochemical methods a guide to modern techniques of plant analysis. Springer Science and Business Media; 1998.
Zou G-S, Li S-J, Zheng S, Pan X, Huang Z. Lemon-Peel extract ameliorates rheumatoid arthritis by reducing xanthine oxidase and inflammatory cytokine levels. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng. 2018;93:54-62.
Saad RA, EL-Bab MF, Shalaby AA. Attenuation of acute and chronic liver injury by melatonin in rats. J Taibah Univ Sci. 2013;7:88-96.
Ayoub SS. Paracetamol (acetaminophen): A familiar drug with an unexplained mechanism of action. Temperature. 2021;8:351-71.
Adio WS, Yinusa IO, Adesola RO, Olawale LA, Moradeyo AT, Ademilua A. Effects and treatments of paracetamol toxicity. World Sci News. 2022;170:69-84.
Stefanello ST, de Carvalho NR, Reis SB, Soares FAA, Barcelos RP. Acetaminophen Oxidation and Inflammatory Markers-A Review of Hepatic Molecular Mechanisms and Preclinical Studies. Curr Drug Targets. 2020;21:1225-36.
García‐Román R, Francés R. Acetaminophen‐Induced Liver Damage in Hepatic Steatosis. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2020;107:1068-81.
Zeb A. Concept, mechanism and applications of phenolic antioxidants in foods. J Food Biochem. 2020;44:e13394.
He F, Ru X, Wen T. NRF2, a transcription factor for stress response and beyond. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:4777.
Ndrepepa G. Aspartate aminotransferase and cardiovascular disease-a narrative review. J Lab Precis Med. 2021;6.
Hong M, Liu H, Chen G, Zhu J, Zheng S, Zhao D, et al. Oridonin alters hepatic urea cycle via gut microbiota and protects against acetaminophen-induced liver injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021; 2021.
Contreras-Zentella ML, Hernández-Muñoz R. Is liver enzyme release really associated with cell necrosis induced by oxidant stress? Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016; 2016.
Senior JR. Alanine aminotransferase: a clinical and regulatory tool for detecting liver injury-past, present and future. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2012;92:332-9.
Patel TB, Olson MS. A reexamination of the role of the cytosolic alanine aminotransferase in hepatic gluconeogenesis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985;240:705-11.
Sharma U, Pal D, Prasad R. Alkaline phosphatase: an overview. Indian J Clin Biochem. 2014;29:269-78.
Poupon R. Liver alkaline phosphatase: a missing link between choleresis and biliary inflammation. Hepatology. 2015;61:2080-90.
Vitek L, Hinds TD, Stec DE, Tiribelli C. The physiology of bilirubin: health and disease equilibrium. Trends Mol Med. 2023;29:315-28.
Guerra Ruiz AR, Crespo J, López Martínez RM, Iruzubieta P, Casals Mercadal G, Lalana Garcés M, et al. Measurement and clinical usefulness of bilirubin in liver disease. Adv Lab Med En Med Lab. 2021;2:352-61.