Evaluation of the Antidiabetic Activity of Hesperidin on Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes Mellitus in Swiss Albino Mice
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/fra.2023.1.8Keywords:
Antidiabetic activity, Hesperidin, Streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus, Glucose reductionAbstract
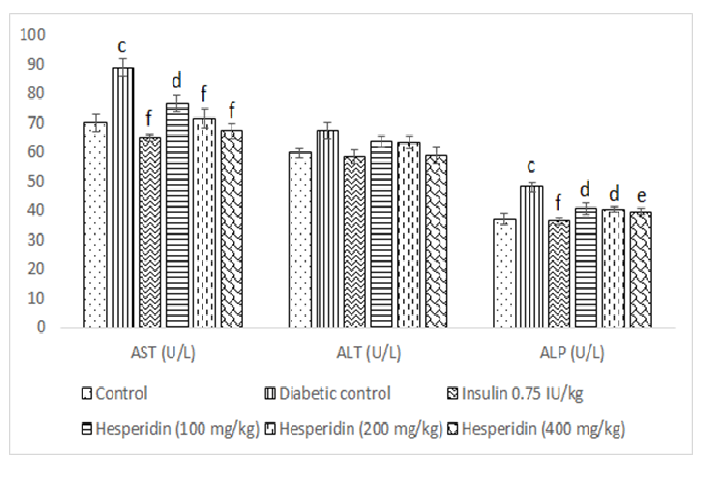
Objectives: The study is planned to investigate the antidiabetic activity of hesperidin on Streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetes mellitus in Swiss Albino mice. Materials and Methods: The Swiss Albino mice were divided into six groups viz., normal control, diabetic control, insulin 0.75 IU/kg, hesperidin 100, 200 and 400 mg/kg, respectively (n = 6/group). All groups received treatments once daily for 21 consecutive days, except normal and diabetic control groups. The random blood glucose and body weight were determined on the pre-study day, 7, 14 and 21st day of the experiment. At the end of the study, blood samples were collected through the retro-orbital plexus puncture and used for the biochemical analysis. Results: Throughout the study, the diabetic control mice showed a significant increase in glucose level when compared with that of the control group, whereas the animals treated with insulin or hesperidin showed a significant reduction in the levels of glucose when compared with that of the diabetic control group. In biochemical analysis, the mice administered with the STZ showed a significant increase in the levels of AST, ALP and creatinine when compared with that of the control group. The mice administered with insulin or hesperidin showed a significant decrease in the AST and ALP when compared with that of the diabetic control group. Conclusion: Hesperidin showed significant antidiabetic activity on STZ-induced diabetes mellitus in mice.
Downloads
Metrics