Assessment of antioxidant enzymes and free radical scavenging activity of selected medicinal plants
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ax.2012.3.8Keywords:
Antioxidant activity, Ascorbate peroxidase, Catalase, Superoxide dismutase, Phytochemical screeningAbstract
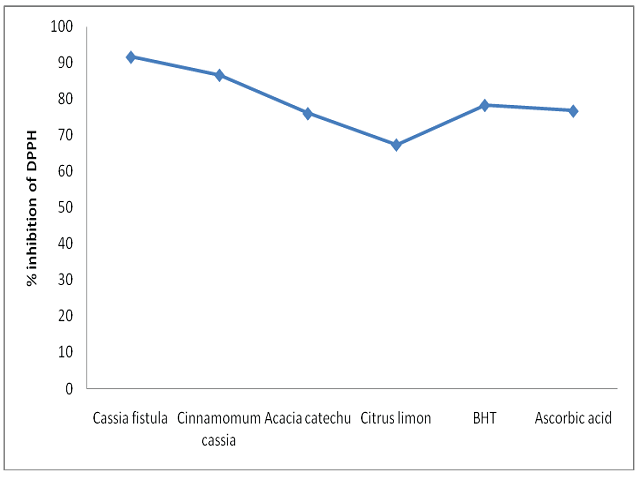
Indian medicinal plants (Cassia fistula, Cinnamomum cassia, Acacia catechu and Citrus limon) were analyzed to study their antioxidant activity. Preliminary phytochemical screening revealed that C. fistula and C. cassia are fairly richer source of alkaloids and flavonoids than the others plants while least amount of Saponins, tannins and terpenoids were observed in all studied plants. The highest free radical scavenging activity was observed in Cassia fistula (91.66 ± 4.33) whereas the lowest was noted in Citrus limon (67.33 ± 3.33). The activities of enzymatic antioxidants: superoxide dismutase, catalase, ascorbate peroxidase, glutathione reductase and polyphenol oxidase were assayed and found significantly higher (P < 0.05) i.e. 2.29, 1.196, 0.746, 0.951 (units/g dry tissues) and 15.15 (min/g dry tissue) respectively in Cassia fistula than the others, where C. cassia was recorded next plant in order to be better-off in the entire enzyme activity assessed except ascorbate peroxidase. The results provided the evidence that the studied medicinal plants are to be potent source of natural antioxidant and medicinally important compounds.
Downloads
Metrics