Antibacterial and Free Radical Scavenging Activity of Michelia champaca Linn. Flower Extracts
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ax.2012.2.10Keywords:
Michelia champaca, Antioxidant, Antibacterial activity, Catechin, AmpicillinAbstract
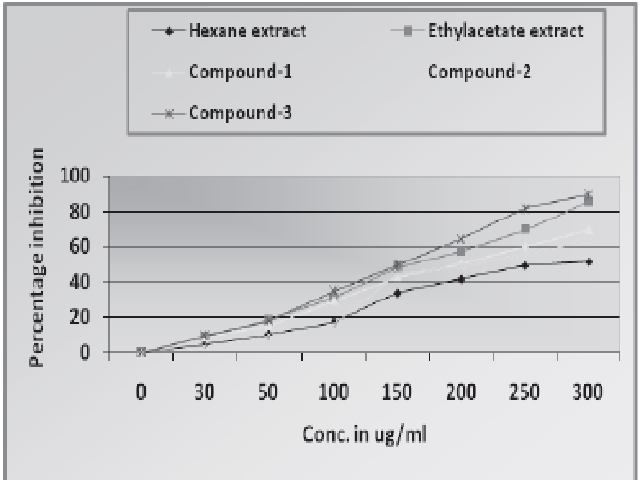
Introduction: Michelia champaca (Magnoliaceae) is a medicinal plant of paramount importance which is traditionally used against a number of diseases including inflammatory conditions. In the present study, crude hexane, ethyl acetate extracts and compounds 1-3 isolated from the extracts of M. champaca flower were investigated for possible antioxidant and antibacterial activity. Method: The DPPH radical scavenging assay was carried out by the protocol given by Nickavar et al 2006.[1] The extracts and the compounds were also investigated for antibacterial activity through disc diffusion method against four different bacterial strains viz. Bacillus subtilis, Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella typhi and Shigella dysenteriae using ampicillin as control. Results: In the present study the ethyl acetate extract, hexane extract exhibited strong antioxidant activity and the IC50 values in DPPH radical scavenging assay were found to be 160 μg/ml and 250 μg/ml, respectively while the IC50 values of isolated compounds 1-3 were 200 μg/ml, 220 μg/ml and 150 μg/ ml, respectively. In this bioassay the extracts showed significant results compared to the individual isolated compounds. Ethyl acetate extract was more effective against all the bacterial strains followed by the hexane extract, compound-3, compound-1 and compound-2. Results of the present study suggest that M. champaca flower extracts and the isolated compounds possess strong antioxidant and antibacterial activity.
Downloads
Metrics