In-vitro Antioxidant Potential of Methanolic Extracts of Mirabilis jalapa Linn
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ax.2011.4.13Keywords:
ABTS radical, DPPH, Free radical scavenging, Mirabilis jalapa, Reductive capacity, Total flavonoidsAbstract
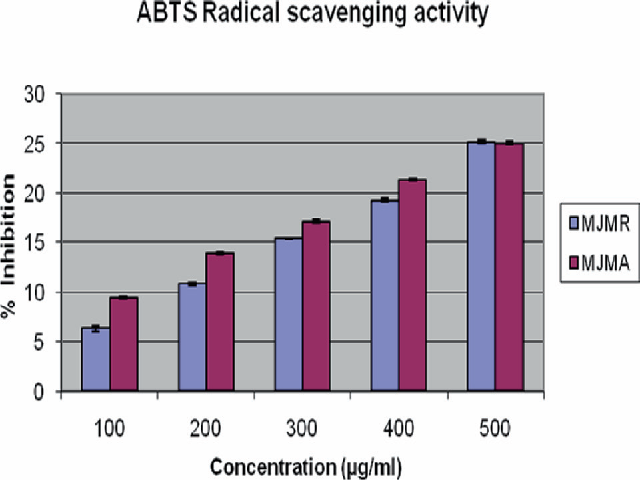
Introduction: Over the past decade, herbal and ayurvedic drugs have become a subject of world importance, with both medicinal and economical implications. The relatively lower incidence of adverse reactions to plant preparations compared to modern pharmaceuticals is encouraging both the consuming public and national health care institutions to consider plant medicines as alternatives to synthetic drugs [1, 2, 3, 4] . Various crude extracts of Mirabilis jalapa Linn of family Nyctaginaceae has been widely used in traditional medicine. The infusion or decoction of Mirabilis jalapa Linn leaves is being used to treat inflammatory and painful diseases [5, 6]. Of date there has not been any report on any kind of antioxidant screening of the areal extracts of Mirabilis jalapa Linn including the kernel and the leaves. Methods: This is one of the first studies reporting the antioxidant potential of aerial (bark and leaves) and the root extracts of Mirabilis jalapa separately using ABTS and DPPH assay methods The present study was aimed to extract, identify the various phytochemical constituents and to study the antioxidant activities of the plant by various chemical and instrumental methods. Results: The extracts showed the presence of alkaloids, tannins, phytosterols, triterpenoids and flavonoids in significantly detectable amounts. In the present study we examined the antioxidant effects of methanolic extract of the aerial parts and root extracts of Mirabilis jalapa Linn at various concentrations in the ABTS+ (2,2’-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulphonic acid ) and DPPH (1,1-Diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl) free radical scavenging assay. Conclusions: The results of the study reveal the immense potential of the plant for further research that aims at identifying the bioactive components responsible for the anti-oxidant activity and elucidating their tentative mechanisms of action.
Downloads
Metrics