Phytochemical Analysis and in vitro Antioxidant Activity of Zingiber officinale
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ax.2011.4.12Keywords:
Antioxidant, Ascorbic acid, DPPH, Zingiber officinaleAbstract
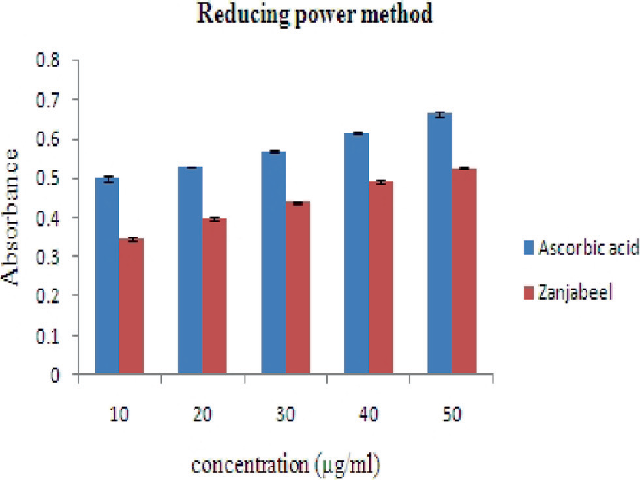
Introduction: Antioxidant activity of the methanol extract of Zingiber officinale was determined by Reducing power assay, Superoxide anion scavenging activity assay, Hydroxyl radical scavenging activity assay, Nitric oxide scavenging activity assay, DPPH free radical scavenging assay, and hydrogen peroxide method. Methods: Preliminary phytochemical screening revealed that the extract of Z. officinale possesses flavonoids, volatile oil and phenolic materials. In the present investigation, quantitative estimation of flavonoids and phenols was carried out by colorimetric methods, using aluminum chloride method and Folin Ciocalteu reagent respectively. Result: The extract showed significant activities in all antioxidant assays compared to the standard antioxidant in a dose dependent manner and remarkable activities to scavenge reactive oxygen species (ROS) may be attributed to the high amount of hydrophilic phenolics. The IC50 values of all parameters were determined while ascorbic acid was used as standard. Conclusion: The results obtained in the present study indicate that Z. officinale extract is a potential source of natural antioxidant.
Downloads
Metrics