Free Radical Scavenging and Anti-lipid Peroxidative Effects of a Hydro-ethanolic Extract of the Whole Plant of Synedrella nodiflora (L.) Gaertn (Asteraceae)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ax.2011.3.10Keywords:
Synedrella nodiflora, Antioxidant, Linoleic acid, Autoxidation, N-propyl gallate, Phosphomolybdenum, Folin-Ciocalteau, DPPHAbstract
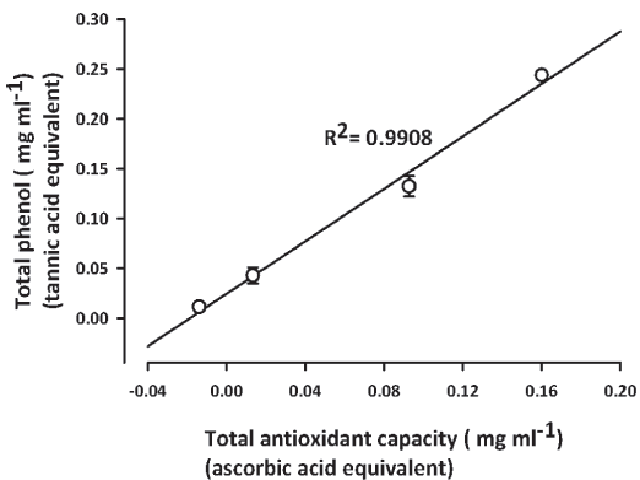
Background: Synedrella nodiflora (L.) Gaertn. (Asteraceae), a native Ghanaian shrub, has been used for the treatment of epilepsy, hiccup and threatened abortion. The present study aimed at investigating the possible mechanisms of antioxidant effects of the hydro-ethanolic extract of the whole plant. Methods: Total phenolic content was determined using the Folin- Ciocalteau assay and the antioxidant capacity by the phosphomolybdenum method. The antioxidant activity was evaluated by the 1, 1-diphenyl-2-picryl-hydrazyl (DPPH) scavenging assays, reducing power assay and inhibition of linoleic acid peroxidation and lipid peroxidation in pentylenetetrazole (PTZ)- kindled rat brains. Results: The extract (0.1-3.0 mg ml-1) was found to contain phenolic compounds which could be responsible for the antioxidant properties since the coefficient of correlation between the Total Phenolic Content (TPC) and the Total Antioxidant Capacity (TAC) was high (r2 = 0.9908). Both n-propyl gallate (0.001-0.03 mg ml-1), a reference antioxidant and the extract (0.1-3 mg ml-1) exhibited antioxidant properties by reducing Fe3+ to Fe2+ in the reducing power test, scavenged DPPH free radicals and effectively inhibited linoleic acid autoxidation and also inhibited lipid peroxidation in PTZ-kindled rat brains. Conclusions:These findings suggest that hydro-ethanolic extract of Synedrella nodiflora contains antioxidant principles which may contribute to its traditional use in epilepsy management.
Downloads
Metrics