Chemical constituents, in vitro antioxidant and antimicrobial potential of Caryota urens L.
Keywords:
C. urens , Antioxidant activity , Antimicrobial activity , ABTS , GCeMSAbstract
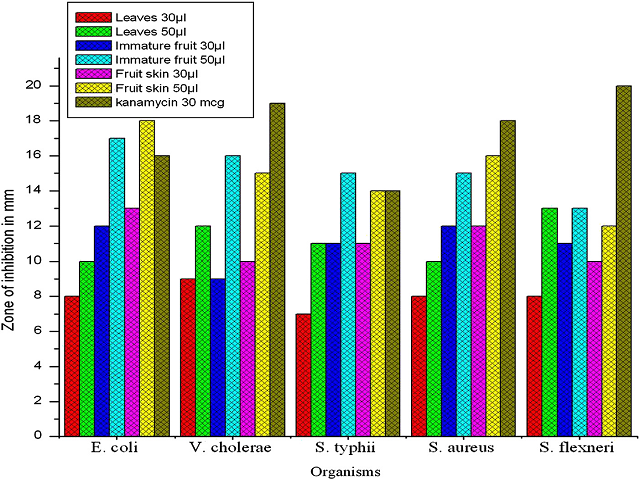
Objective: To evaluate chemical constituents, in vitro antioxidant and antimicrobial potential of Caryota urens L. Methods: Qualitative analysis of crude extract of C. urens was carried out by gas chromatography mass spectrometry (GCeMS) method and their in vitro antioxidant activity was evaluated using DPPH, ABTS, reducing power and nitric oxide scavenging assays. Antimicrobial activity was determined by disc diffusion method. Results: GCeMS analysis showed the presence of fatty acids, aliphatic, aromatic and phenolic acids. The antioxidant activity of immature fruit and leaf extracts yielded high activity when compared to the fruit skin. The fruit skin and immature fruit of C. urens exhibited strong antibacterial activity against the tested pathogens (Escherichia coli, Vibrio cholerae, Salmonella typhii, Staphylococcus aureus and Shigella flexneri) when compared to leaf. Conclusion: In our results, we suggest that C. urens extracts have strong antioxidant and antimicrobial potential. The identified bioactive compounds of C. urens could be attributed to antioxidant and antimicrobial property.
Downloads
Metrics