Efficacy of treatment on antioxidant status in cervical cancer patients: A case control study
Keywords:
Antioxidant enzymes , Cervical cancer , Chemotherapy , Free radicals , Lipid peroxidationAbstract
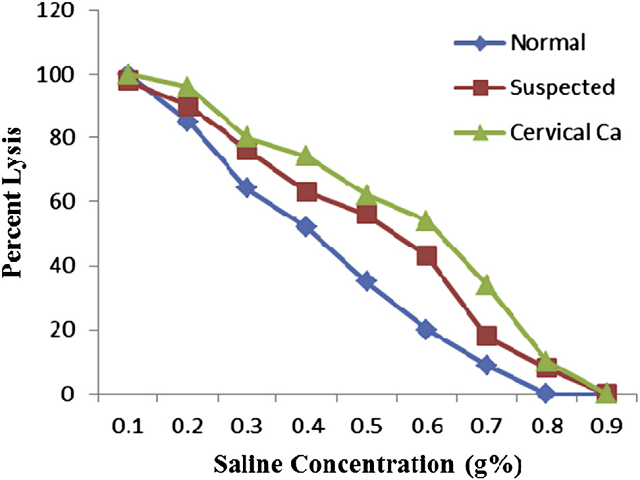
Background and aim: To evaluate the effect of treatment on antioxidant status of cervical cancer patients with suspected and healthy. Method: The study was included 59 cancer patients with cervical cancer were compared to suspected (n = 25) and healthy controls (n = 25). Of the 59, 30 patients undergoing chemotherapy alone, for 3 months and 29 patients were undergoing radiotherapy along with chemotherapy. Blood samples were collected after the treatment from all the groups and estimated the level of serum malondialdehyde, non-enzymatic antioxidant glutathione and enzymatic antioxidant including super oxide dismutase, catalase, glutathione peroxidase, glutathione reductase, glutathione-S-transferase and glucose-6- phosphate dehydrogenase. Results: The levels of serum malondialdehyde and glutathione reductase were significantly (P < 0.05) increased and all antioxidant enzymes were decreased in cervical cancer patients when compared to normal controls and suspected cases. The estimated antioxidant status was increased significantly after the treatment of radiotherapy along with chemotherapy than the chemotherapy alone. Conclusion: The results suggest that the elevated lipid peroxidation and impaired antioxidant status was significantly increased after the radiotherapy with chemotherapy than the chemotherapy alone.
Downloads
Metrics