Antioxidant activity and the effect of different parts of areca catechu extracts on Glutathione-S-Transferase activity in vitro
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ax.2011.1.6Keywords:
Areca catechu, Antioxidant Activity, GST, DPPH, Total phenolic compoundsAbstract
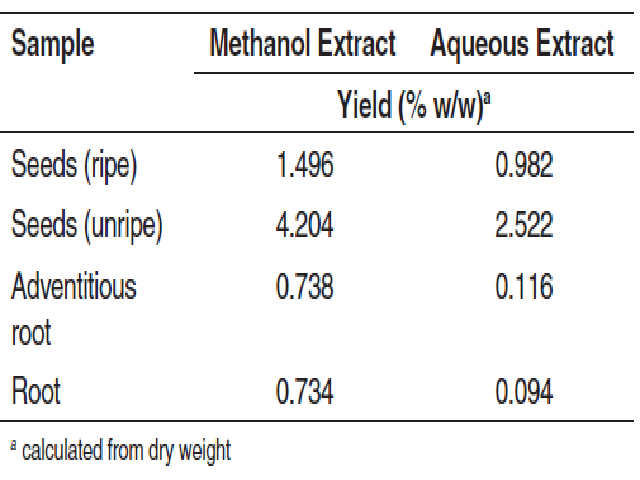
Areca nut (Areca catechu L.) or Pinang is one of the most widely used psychoactive substance with several hundred million users worldwide, predominantly in Southern Asia. This study evaluates the antioxidant activity and the total phenolic compound of methanolic and aqueous extract of seeds (ripe and unripe seeds), root and adventitious root. The antioxidant activity was determined using the 1, 1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical scavenging assay and total phenolic using the Folin-Ciocalteu method. The results from this study showed that the antioxidant activities of the water and methanolic extracts of the seeds as determined by the 1, 1-Diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) presented higher percentage inhibition than the root and adventitious root. The methanol extracts gave higher antioxidant activities than the aqueous extracts and comparable to that BHT and Vitamin C. The results also showed that unripe seeds methanolic extract possessed higher content of phenolic (186.2 ± 0.04 mg GAE/g) and total flavonoid (18.13 ± 0.007 mg/g) than other parts of A. catechu. We also evaluated the in vitro effect of various A.catechu methanolic and aqueous extract on the activity of Phase II metabolizing enzyme, glutathione-S-transferase (GST) in rat liver. Unripe seeds methanolic showed the effective GST specific activity inhibition with an IC50 of 115.05 μg/mL with maximum inhibition >70%. These results suggest that areca nut extracts have the potential to prevent oxidative damage in normal cells due to their antioxidant characteristics.
Downloads
Metrics