Protective Role of Kaempferol Against Acrylamide Intoxication
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/fra.2017.1.6Keywords:
Carcinogenic, Flavonoid, Neurotoxic, Oxidative stress, AntioxidantAbstract
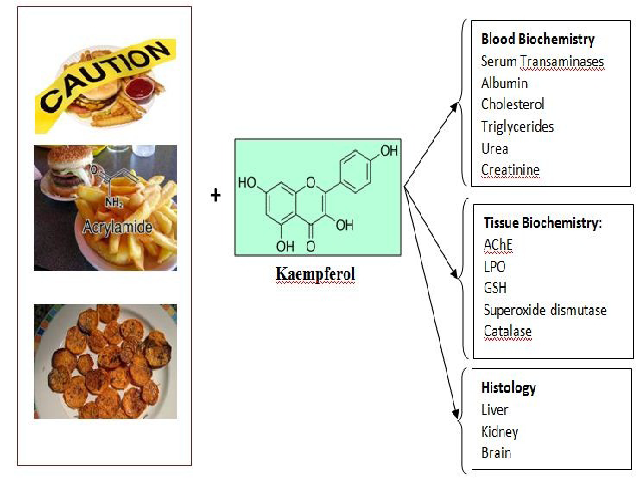
Background: In present scenario Acrylamide (A) concentration in starchy food processed at high temperatures have become very serious health problems. It is also used in industries and research chemical and potent toxic to experimental animals as well as humans. The present study was carried out to investigate protective effects of Kaempferol (KPF) against A-induced toxicity in rats. KPF is a natural flavonol, found in tea, strawberries, broccoli, cabbage, beans, grapes, tomato and plant products used in traditional medicine such as ginkgo biloba, Moringa oleifera and propolis. Methods: A (38.27 mg/kg, p.o.) was administered to female Wistar rats for 10 consecutive days followed by therapy of KPF for 3 days at different doses (5, 10, 20, 40 mg/kg, p.o.). Results: Activities of transaminases (aspartate aminotransferase/alanine aminotransferase), urea, creatinine and lipid profile were significantly rise whereas decline in haemoglobin after A administration. A significant elevation of LPO were observed with concomitant depleted activities of SOD, CAT and GSH in toxicant treated group. Significant reduction was found in the activity of AChE in brain. Therapy of KPF showed its protective effect on biochemical and histopathological observation at all the doses in a dose dependent manner. Conclusion: The protective effect of KPF was observed against A-induced toxicity.
Downloads
Metrics