Isolation, Structure Elucidation of Ferulic and Coumaric acids from Fortunella japonica Swingle leaves and their Structure Antioxidant activity Relationship
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/fra.2017.1.4Keywords:
Fortunella japonica, Coumaric acid, Ferulic acid, Hepatocytes, Antioxidant, HepatoprotectiveAbstract
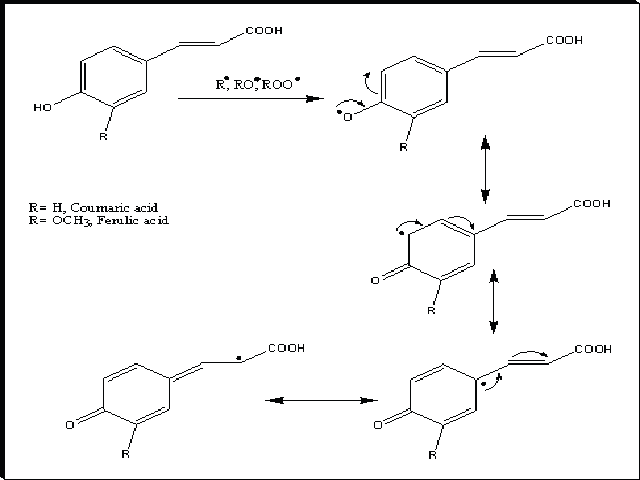
Objective: The present study deals with isolation, structure elucidation of ferulic and coumaric acids from Fortunella japonica Swingle leaves and their structure antioxidant activity relationship. Structural analysis was conducted using UV, IR, mass and Nuclear Magentic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. Methodology: In particular, completely assigned 1H and 13C-NMR data are presented. Also, the present study was extended to investigate the hepatoprotective activity of isolated compounds against paracetamol-induced toxicity in freshly isolated rat hepatocytes model. Freshly isolated rat hepatocytes were exposed to paracetamol (5 mM) along with/without various concentrations of the isolated compounds (40–80μg/ml). Results and Discussion: Exposure of isolated hepatocytes to paracetmol resulted in lipid hydroperoxides formation, depletion in protein thiols, superoxide dismutase (SOD), succinate dehydrogenase (SDH), catalase (CAT), glutathione peroxidase (GPx) and glutathione reductase (GR) levels as well as elevation of alanine transaminase (ALT), aspartate transaminase (AST), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and alkaline phosphatase (ALP). The isolated coumaric and ferulic acids have been found to efficiently inhibit paracetamol-induced biochemical alterations, namely oxidative stress biomarkers and protein oxidation. It also significantly prevented paracetamol-induced loss in the activity of antioxidant enzyme and the important endogenous antioxidant glutathione. Conclusion: The study suggests that coumaric and ferulic acids can act as an antioxidant and hepatoprotective in physiological systems.
Downloads
Metrics