Polarity-dependent Response of Phytochemical Extraction and Antioxidant Potential of Different Parts of Alcea rosea
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/fra.2022.2.9Keywords:
Alcea rosea, Antioxidant potential, Phytochemical composition, Solvent polarity, Free radical scavenging activityAbstract
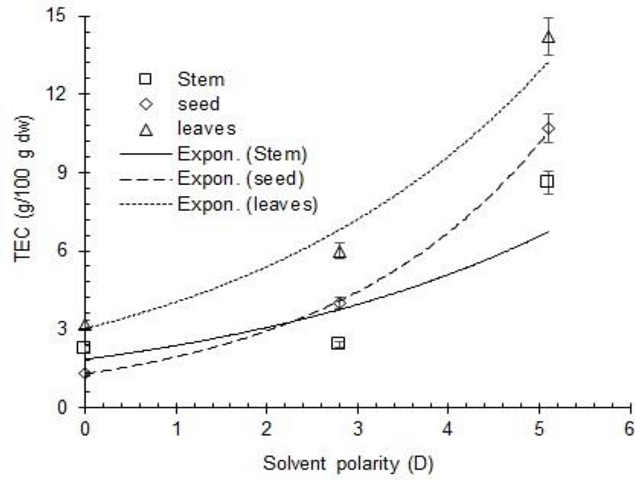
Objectives: Alcea rosea is a good source of medicinlly importeant bioactive phytochemical compounds. The complete extraction of these biochemicals from plant material has remained a problem for the researchers and manufacturers. This study was planned to report the medicinal value of A. rosea and find out the suitable extraction solvent to enhance the extraction yield of its phytochemical compounds and their antioxidant potential. Materials and Methods: The powdered samples of the selected parts of A. rosea were extracted in solvents of varying dipole moments (hexane: 0 D, ethyl acetate: 2.8 D, and methanol: 5.1 D). The extracts were screened for the presence of important phytochemicals and analyzed for their phytochemical content and antioxidant potential. Results: The studied parts of A. rosea consisted of flavonoids, tannins, terpenoids, saponins, and cardiac glycosides. The regression analysis showed polarity-dependent significant positive effects (p<0.05) on the extract yield, phenolic content, and antioxidant activity in terms of Trolox equivalent total antioxidant activity, ferric reducing power, and nitrogen free radical scavenging activity of the extracts. However, a mixed response of total flavonoids and total tannins content and hydroxyl radical scavenging activity of the extracts was observed against solvent polarity. Conclusion: A polarity dependent increase in phytochemical content and free radical scavenging capacity was observed. The study suggests that the polar solvents are more suitable to achieve a good extract yield of phytochemicals possessing a strong antioxidant ability and the solvents of medium polarity may be suitable for the extraction of flavonoids and tannins from the studied parts of A. rosea.
Downloads
Metrics