In vitro anti-cancer and anti-oxidant activity of different fractions of Diospyros peregrina unripe fruit extract
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ax.2012.4.8Keywords:
Anti-oxidant, Diospyros peregrina, Free radicals scavenging, In vitro cytotoxicityAbstract
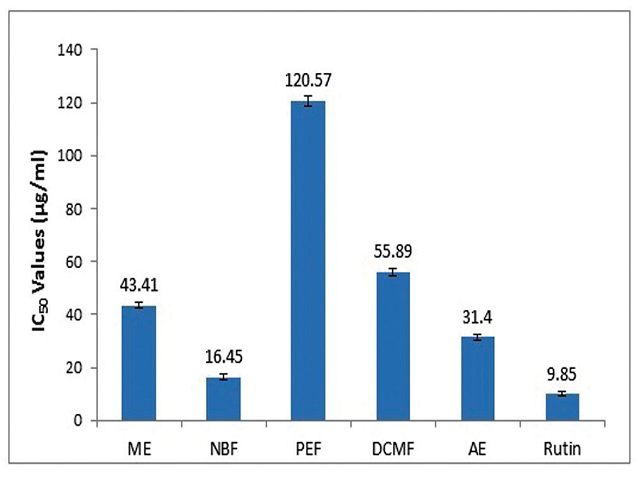
Background: Diospyros peregrina (Ebenaceae) is a medium-sized evergreen tree having ethnomedicinal significance as an aphrodisiac, astringent, bactericide and for the treatment of diarrhoea, cholera, dysentery, fever, malaria and diabetes. Objectives: To evaluate the anti-oxidant and anti-cancer activity of different extracts and fractions of matured unripe fruits of Diospyros peregrina on various in vitro models. Materials and Methods: Anti-oxidant and free radical scavenging activity of various extracts and fractions were determined by DPPH, ABTS and Alkaline DMSO methods. In vitro cytotoxicity of different extracts and fractions of matured unripe fruits of Diospyros peregrina was evaluated on MCF-7 and Hep-G2 cell lines by MTT and SRB methods. Results: Among the extracts and fractions studied for antioxidant activity n-butanol fraction (NBF) and aqueous extract (AE) showed potential scavenging effect against DPPH, ABTS and superoxide free radicals. In vitro cytotoxicity assays of extracts and fractions by MTT and SRB methods revealed that dichloromethane fraction (DCMF) exhibited maximum cytotoxicity on both MCF-7 and Hep G2 cell lines. Conclusion: The higher anti-oxidant potential of n-butanol fraction (NBF) and aqueous extract (AE) may be due to the presence of phenolic compounds, flavonoids or flavonoid glycosides. Dichloromethane fraction (DCMF) exhibited maximum cytotoxicity on both MCF-7 and Hep G2 cell lines. The cytotoxic activity of DCM fraction may be attributed due the presence of triterpenoids.
Downloads
Metrics