Protective effect of Ficus bengalensis L. extract against H2O2 induced DNA damage and repair in neuroblastoma cells
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/fra.2014.1.2Keywords:
Neurodegenerative diseases , Ficus bengalensis extract, DNA damage and repair , Oxidative stress , NeuroprotectionAbstract
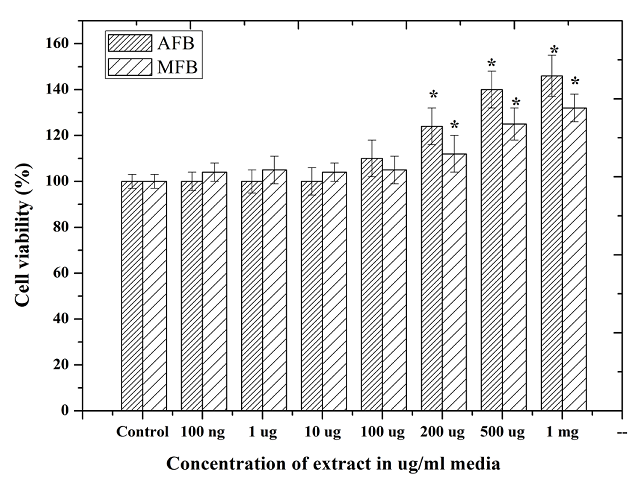
Aim & background: Neuronal cells, because of their high rate of oxidative metabolism and low levels of antioxidants, are quite susceptible to oxidative DNA damage. Ficus bengalensis L. (Banyan tree) is a large tree and possessing medicinal properties. The study was designed to investigate the protective effect of Ficus bengalensis (FB) extracts against H2O2 induced DNA damage and repair in human neuroblastoma cells (SK N SH). Methods: Aqueous and methanol extracts of Ficus bengalensis were prepared and cell viability conferred by these plant extracts was evaluated by MTT assay. DNA damage and protection by FB extracts was measured by comet assay using H2O2 as DNA damaging agent. Results: Cell viability markedly decreased with increased DNA damage after a 24 h exposure to H2O2. However, prior incubation with FB extract (0.1 – 1.0 mg/ml) for 24 h, and then exposed to H2O2, cellular toxicity was significantly attenuated in a dosedependent manner. Oxidative DNA damage in FB treated cells showed a significant reduction in intensity of DNA damage in terms of comet tail length and also brought to control level. Conclusion: The study indicated Ficus bengalensis extract showing potential neuroprotective activity against oxidative environment generated by H2O2 treatment.
Downloads
Metrics