Antioxidant capacity and phenolic content of Elaeagnus kologa schlecht. an underexploited fruit from India
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ax.2012.3.4Keywords:
Antioxidant activity, Elaeagnus kologa, Lipid peroxidation, Reductive capacity, Total phenolics, Total flavonoidsAbstract
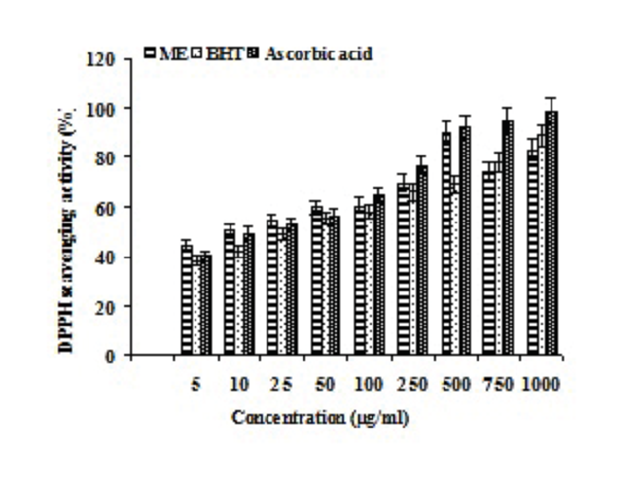
Introduction: In this study, assessment of total phenolic and flavonoid contents and antioxidant capacity of methanolic extract of fruits of Elaeagnus kologa Schldl. were examined for the first time. Methods: For the determination of total phenolics (TP) and total flavonoid content (TF) and in vitro antioxidative capacity, established assay methods such as 1, 1-diphenyl – 2-picryl hydroxyl (DPPH) radical assay, reducing power, ferric ion chelating assay, superoxide anion, nitric oxide scavenging activity and reduction of lipid peroxidation assays were used with reference to synthetic antioxidant butyl hydroxyl toluene (BHT). One way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Duncan’s Multiple Range Test (DMRT) were carried out. Results: The extract yielded total phenolic content (TP) of 2120 ± 0.012 mg gallic acid equivalents (GAE)/100 g of fresh mass (FM) and total flavonoid content (TF) of 220 ± 0.12 mg quercetin equivalents (QE)/100 g FM. The E. kologa fruit exhibited scavenging capacity towards DPPH∙, superoxide radical, hydroxyl and nitric oxide. The results also showed that E. kologa extract had a strong reductive capacity, strong ferric ion (Fe3+) chelation and remarkable reduction of lipid peroxidation. The antioxidant capacities of the extract were comparable with butyl hydroxy toluene, EDTA and catechin. Conclusion: Positive correlations were observed between polyphenolic contents and the antioxidant capacities. The results of the present study revealed that the fruits of E. kologa possess potent antioxidant activity.
Downloads
Metrics