Electrophilic, Free Radical and Reactive Oxygen Species Scavenging and Detoxification Potentials of Lophiraalata Stem Bark Extract
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ax.2011.3.6Keywords:
Lophiraalata, Reactive oxygen species, Free radicals and electrophile detoxifying enzymesAbstract
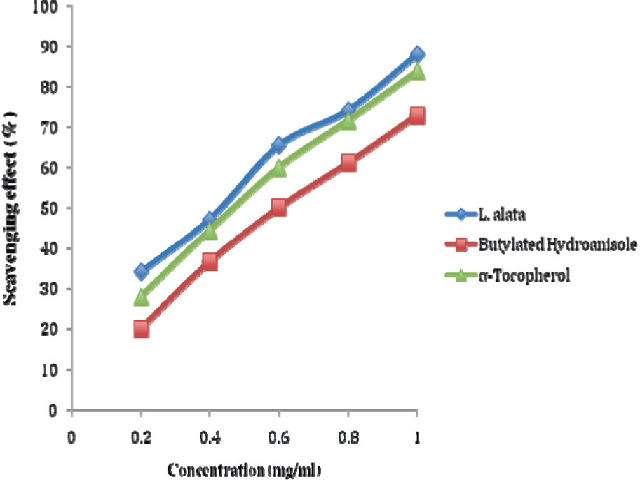
The electrophilic, free radical and reactive oxygen species scavenging and detoxification potentials of Lophiraalata stem bark was evaluated. L. alata stem bark effectively scavenged DPPH radical, superoxideion and hydrogen peroxide. It produced 88% scavenging effect of DPPH radical at a concentration of 1.0 mg/ml. Aqueous extract of L. alata-stem bark produced 76% and 92% scavenging effect on superoxide ion and hydrogen peroxide respectively at 1.0 mg/ml, which compared favourably with the synthetic antioxidant (butylated hydroanisole and α-tocopherol). A reducing power of L. alata stem bark was examined using K3Fe(CN)6, 2-folds reducing power potentials was exhibited by L. alata stem bark when compared with the synthetic antioxidant,butylated hydroanisole. Reactive oxygen species detoxify enzymes; superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), glutathione peroxidase (GPx) and glutathione reductase (GRed) were significantly induced by 90, 133, 90 and 172% respectively. While the electrophilic detoxifying enzymes NADPH: quinone oxidoreductase-1 (NQO1), uridyl diphosphoglucuronosyl transferase (UGT), glutathione S- transferase (GST) and epoxide hydrolase (EPh)) were induced by 240, 81, 196 and 281% respectively at the end of the experimental period. In view of these properties, L. alata can act as a prophylactic by intervening as electrophilic, free radical and ROS scavenger and detoxifier.
Downloads
Metrics