A Comparative Study of Antioxidant Potential of Three Commonly Used Spices in Bangladesh
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/fra.2018.1.2Keywords:
A. cepa, A. sativum, Z. officinale, Antioxidant PotentialsAbstract
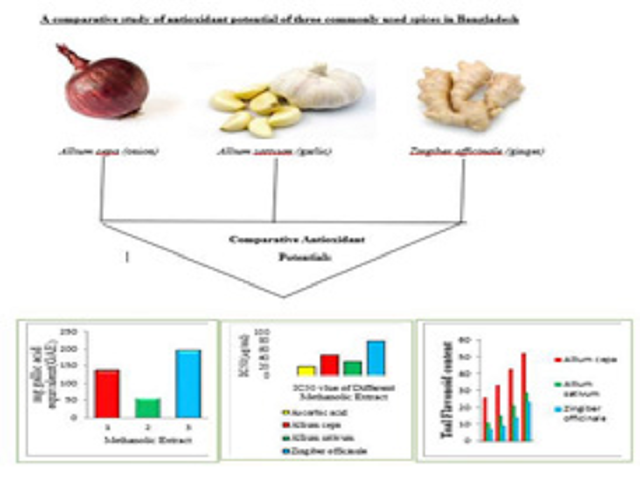
Introduction: Spices like Allium cepa (onion), Allium sativum (garlic), Zingiber officinale (ginger) etc are indispensable part for the preparation of our daily food and are reported to possess compounds, which have varied with beneficial biological effects. Aims: The present study was undertaken to evaluate and compare the antioxidant potentials of ethanolic extracts of A. cepa bulb, A. sativum bulb and Z. officinale rhizome. Methods: All the extracts of these three spices were subjected to total phenolic content, total flavonoid content and DPPH radical scavenging assay for determination of antioxidant activity. Data are tested and tabulated by using SPSS software of 10 version. Results: The present study revealed that Z. officinale extract exhibited the highest DPPH radical scavenging activity (IC50 value of 32.439 (μg/ml)), followed by A. cepa (IC50 value of 48.077 (μg/ml)), and A. sativum (IC50 value of 78.289 (μg/ml)) respectively. The study also supplicated that Z. officinale has higher phenolic but lower flavonoid content at different concentrations than A. cepa and A. sativum. Conclusion: According to our present study it can be summarized that these spices have antioxidant activity and can be used as natural drug sources for the development of potential preventive intervention in case of free radical-mediated diseases. Therefore, consumption of these spices might be helpful in combating the progression of various diseases related to oxidative stress.
Downloads
Metrics